AWS Billing And Cost Optimization; Decoding The Maze!!
When it comes to Billing and Cost Optimization, it feels like a complex concept.Using a case study, we'll go through the basic concepts of Optimizing.
Table of contents
No headings in the article.
Hello my brothers and sisters in AWS!!! Guess who's back!!🥰🥰🥰🥰 Now normally, I would have continued with my AWS Services series, but I have to deviate just a lil' bit!!
Now on May 2nd, I was just chilling at work, pretty boring Monday! I was wondering when the day would end! Then I received a rather surprising email from AWS!!
Sooo..... $6.23 billing statement? At first I was confused. Okay I thought I was on free tier? Then it occured to me! Dang. I had made my own VPN and launched just one instance, but I totally forgot to shut it down until I think several days later! I can't even remember when it was!
Now paying for that $6 really pained me, but then at least I shut it down! Imagine if I had totally forgot to shut the instance down for say the whole month! 🤕🤕🤕 Well I'd have started a GoFundMe fundraising to help me clear that bill!😂😂😂💔 because well, it probably would have been $150 or something. I was so terrified of even breathing around the console!
Now forget about meanie Cyndie who was pained by $6, there's a startup that managed to rack up a whooping $72,000 bill! Imagine being in charge of finance, trying to tell your bosses about that bill 😰😰😰
Now this made me realize that launching services in the cloud is veery easy, but woe unto you when the end month statement comes! This led me to AWS billing and cost optimization. Interestingly, it took me a while to grasp the billing and cost optimization concepts! I don't know if its only me, but why is billing so damn complex!🤔🤔
Anywaaays, let's get back to business! AWS Billing and Cost Optimization is actually a whole discipline on its own, so it might be hard to fully exhaust it today! But through a case study, we can get to grasp atleast the major concepts! So buckle up!
Now we have a hospital, CynHealth. They require AWS services to run a fast and productive EHR (Electronic Health Records), they need a patients' database for easier retrieval of data. They also need a web application to run their online services. Let's design a solution for them, but following the [AWS Well Architected Framework Pillars]
(aws.amazon.com/blogs/apn/the-6-pillars-of-t..)
- Operational Excellence
- Security
- Performance
- Cost Optimization
- Sustainability
- Reliability
1. Organize Member Accounts Using AWS Organizations, IAM Policies and Tag Policies
The first thing would be to ensure everything is in order, before diving into AWS services. Since this is a hospital, we have several teams in play;
- Medical team
- Administrators(IT, Executive)
- Finance team
We'll first create a root account for the hospital. This account will be used as the administrator account in AWS Organizations.
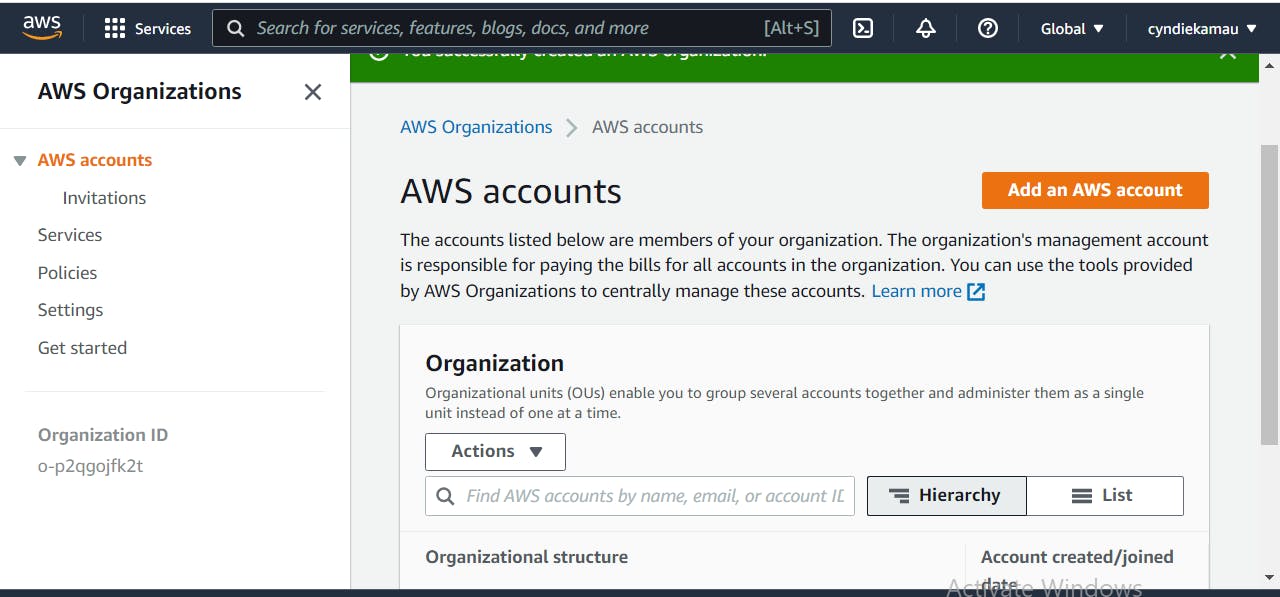
We then create member accounts for the different teams, using AWS Identity and Access Management.
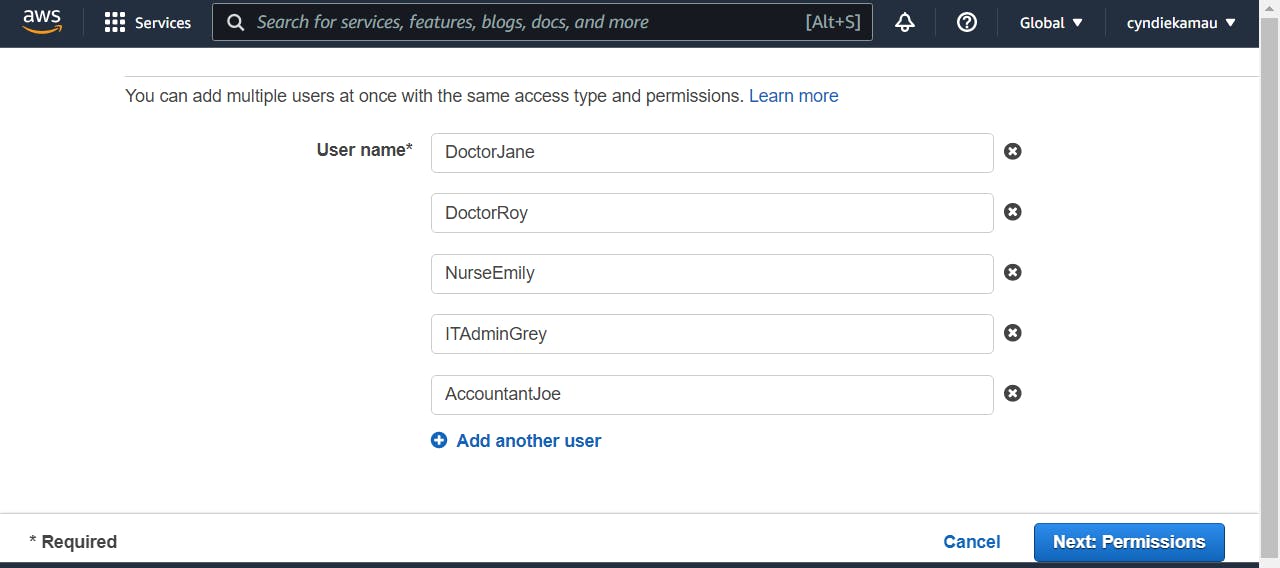
Create a custom password, and for security purposes the users will sign in to the AWS Console using a password, and not access keys. This is because access keys are very sensitive, and once exposed could be exploited!
We'll then create groups for every team. Finance team, Admin team, Medical team, IT team. Each of the individual user accounts will now be grouped into their appropriate groups, and policies will be attached to those groups through a permissions boundary, to control maximum user permissions.
Example,The Executive Admin team has administrator access to the root account, access to the AWS CloudTrail Dashboard the Finance team has access to the AWS Cost Explorer Dashboardbut cannot launch any services , Developer team access to the access key IDs to access the development tools, yeah.
After users are grouped, tags are introduced to every group. Tagging strategies are very important, because the help in monitoring and evaluation. Example, the IT team decides to launch a test virtual machine before production. By labeling the vm, it is easier to monitor to avoid having underlying costs and no one knows who launched what 🤭.
Now using AWS Cost Allocation Tagsonly the admin account can activate the AWS generated CreatedBy tags, so whoever launches anything, it immediately tags. Example;
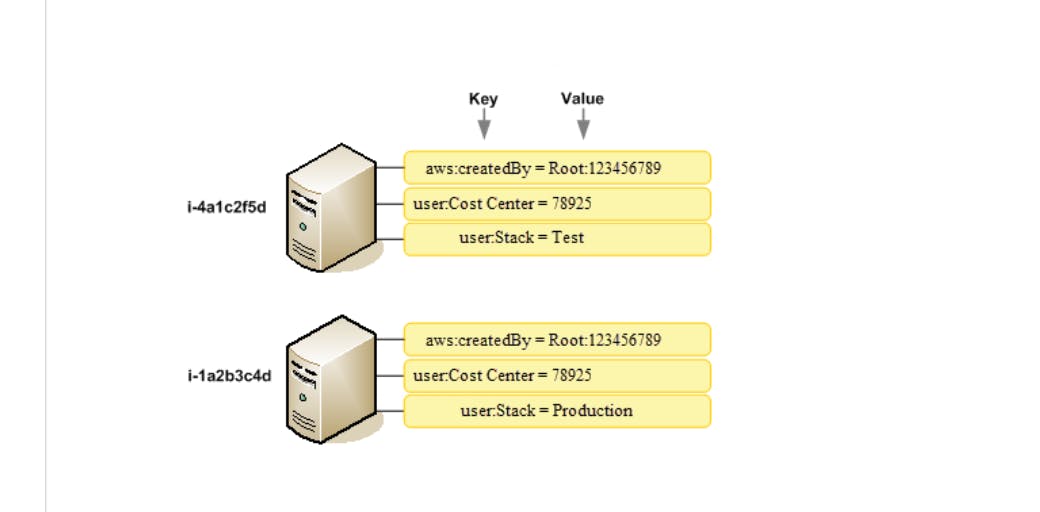 *Image from AWS Documentation
So no hiding! Once you launch say an instance, we are watching hehehe.
*Image from AWS Documentation
So no hiding! Once you launch say an instance, we are watching hehehe.
2. AWS Services
Okay now we've set everyone up. Let's have a look at some of the AWS services our hospital needs.
Compute Services
Okay to quickly explain compute services, imagine accessing an Iphone on a Tekno phone, at 1/8 the cost. That's computing. Accessing powerful machines over the internet at an affordable cost.
Now for our hospital, they need an efficient EHR system. After searching the AWS Marketplace for healthcare solutions, we found the OpenEMR Cloud.
Now what usually happens with compute, you have the virtual machines, right? You are now launching an Operating System online. In simple terms, you have your normal windows, then you launch another windows online, to run softwares in it which you can't run in your home windows without crashing the laptop.
For our case, our operating system will be linux. So we will be launching linux instances (virtual machines) . Note that windows instances are more expensive compared to Linux instances.
Okay with that set, lets shift to the compute billing and cost optimization sector. Now to use OpenEMR Cloud software, we'll launch a Linux instance, right? Let's first understand EC2, starting with its pricing points.
- EC2 Instance Uptime:- Charges are per hr/sec while the EC2 instance is running. So if the Linux instance runs for two days, we'll be charged 48 hours.
- EBS Storage:- So when you are launching an instance, you have to attach storage for it. This storage is known as Elastic Block Storage. You are charged for every storage provisioned, so attaching an 8GiB (Gigibyte) when you only need 4, means you've paid extra for unused resources.
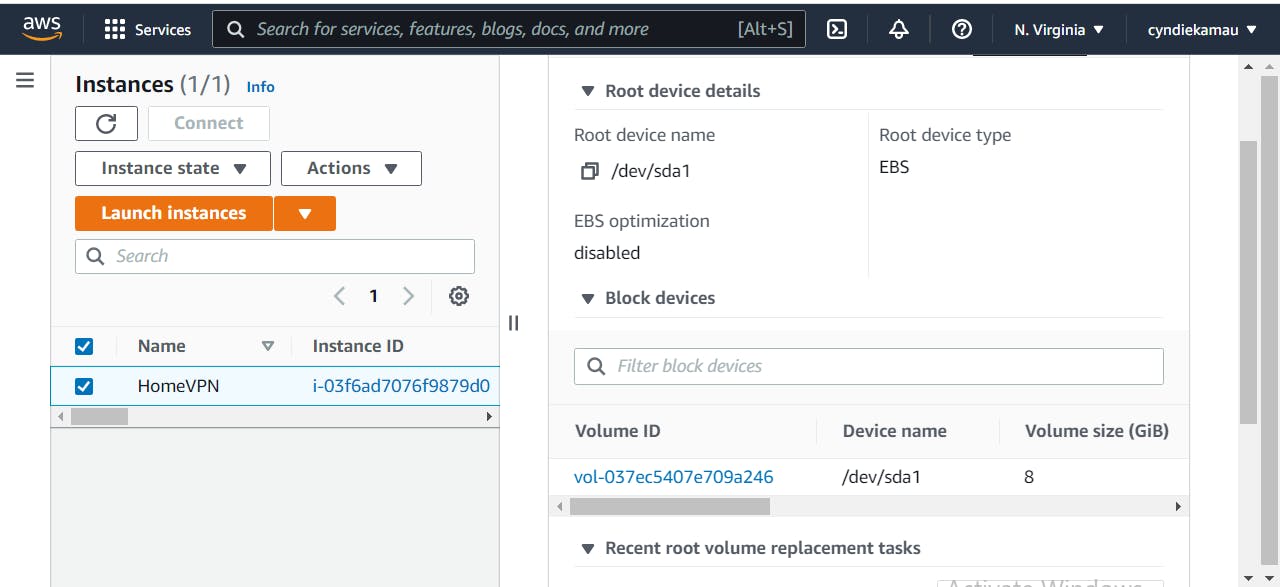
Using my VPN instance as an example, I had provisioned an 8Gib EBS storage for it. Now you might forget everything else, but never forget to click on 'Delete on Termination' icon.
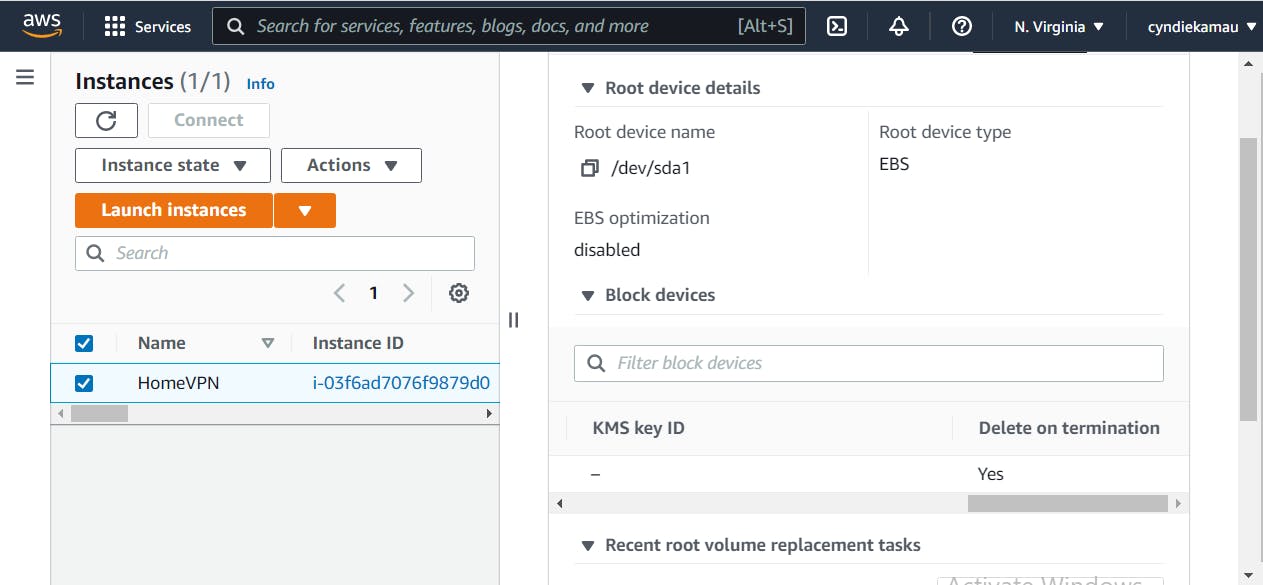
- Data transfer out:- You are also charged for transferring data across AWS regions, or on-premise. Just ensure that as much data as possible stays within the region to avoid extra costs.
Next we'll quickly skim over the types of instances. They are made up of five families;
- General Purpose instances
- Compute Optimized
- Storage Optimized
- Memory Optimized
- Accelerated Computing
You can learn more about them here.
In our case, we will be using the General Purpose instances. (t2) Instance size also matters. Its better to run smaller instances on your workload, than fewer larger ones. In our case, we will use the micro instance size. So our Linux instance size will be t2.micro (t2 for instance type, micro for size)
The last thing to understand when it comes to EC2, is the [purchase options].(docs.aws.amazon.com/AWSEC2/latest/UserGuide..)
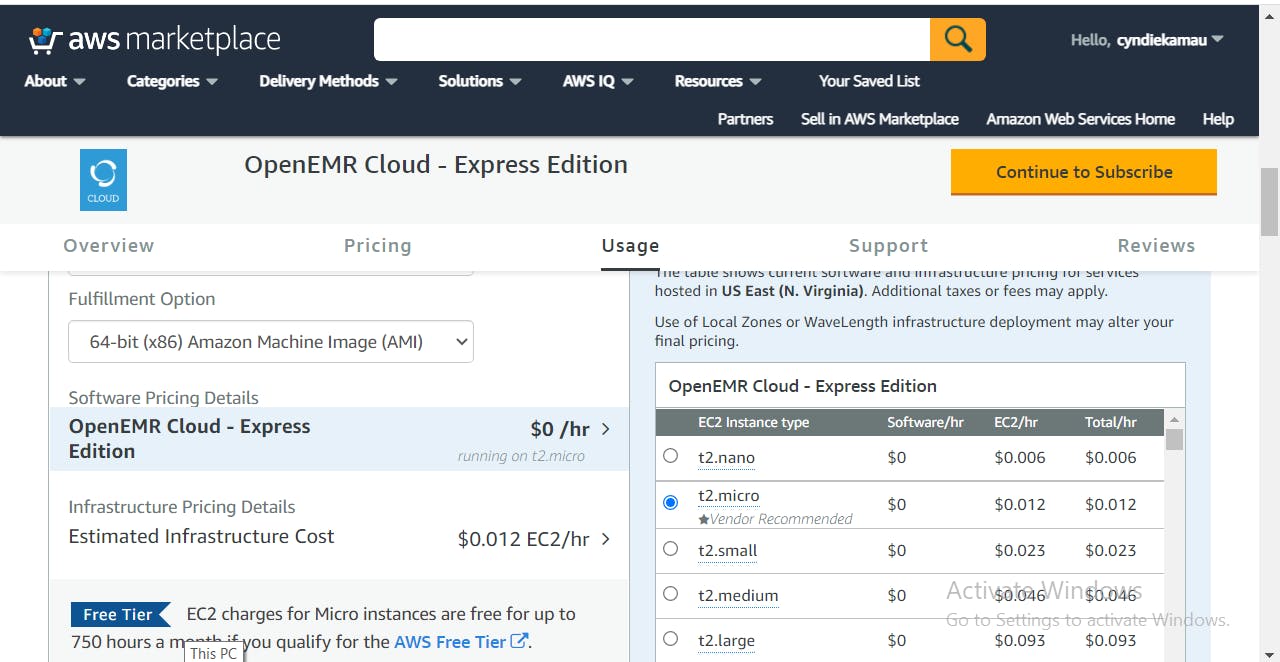
As you can see, the billing is $0.012 per hour. Meaning if we let the instance run for 24 hours for 31 days,it sums up to $8.928. Let's add the EBS storage fee. Let's say we've provisioned 10GB of storage for our instance. Because its a general purpose volume, its $ 0.10 per GB per month. That's $1. So the total cost will be $9.928 per month, for starters.
But remember, as the workload increases, so does the instance capacity and EBS volume. So to monitor the instances to avoid runaway costs, we use several tools:-
- Amazon EC2 Auto-Scaling to set scaling policies, eg the max amount of extra instances to be launched is 4.
-Amazon CloudWatch to monitor the instances, and set up alarms. Incase an extra instance has launched, through Amazon SNS the teams are notified of the change, via email or SMS.
- AWS Cost Explorer for constant resource optimizations
-AWS Trusted Advisor for AWS right-sizing recommendations.
Developers can also launch several test instances before production, so to avoid paying for the servers when they are idle, we use AWS Instance Scheduler to automatically stop instances when not in use, eg during weekends.
Storage Services
CynHealth also needed storage services to store their data, but at an affordable cost. Before we design a solution for them, let's first go through storage. Storage of data usually occurs in an Amazon S3 Bucket as objects. Think of objects as let's say flash drives which we put in a bucket. Now there are several types of storage classes;
Standard Storage Bucket:- This is used for objects with frequent access. Accessing these objects is free, but storage is charged based on object size.
Standard -IA:- Used for objects retrieved occassionally. it's a bit cheaper than standard, but there's an extra charge for accessing the objects.
S3 Glacier:- This is for archive data which is not frequently accessed and needs long-term storage. It has 3 subsets; S3 Glacier Instant Retrieval, S3 Glacier Flexible Retrieval and S3 Glacier Deep Archive.
One Zone-IA:- It is cheaper than standard and -IA, but all your data is restricted to one zone. So in the events the AWS data warehouse burns.... all your data poof! 🤭🤭
Intelligent Tiering:- This is for any data which has different access patterns, so you're not sure where to place it. It automatically places objects in their appropriate classes based on the access analytics. Charges come from transitioning objects between classes.
With that in mind, lets go back to CynHealth. Now they have 10 TB worth of data which they want to store in S3 Buckets. To fully understand the importance of storage classes, we'll have two scenarios; one where they put all their data in a standard storage class, the other where they used storage classes.
Now in a standard storage bucket, remember we said object size affects the charges. So its $0.023 per GB. We have 10 TB (10,000GB) so its $230 per month.
Let's now use storage classes. Based on the data analytics, we divided the data into several classes;
3 TB frequently accessed data
3 TB occassionally accessed data
3 TB rarely accessed data
1 TB data with frequently changing patterns.
Let's place them into their appropriate categories.
- The first 3TB will go to the Standard S3 buckets. That's $0.023 * 3,000 = $69.
- The next 3TB will go to -IA buckets. That's $0.0125 * 3,000 = $37.5
- The third 3TB will go to S3 Glacier Flexible Retrieval. That's $0.0036 * 3,000 = $10.8
- The last 1TB Intelligent Tiering. For general monitoring, automation and storage, its $0.0025 per 1,000 objects. That's $2.5
It sums up to $119.8 ! From $230 ! Now we haven't added retrieval fees yet, so we could estimate it to around $130 per month. We've saved $100!! 🎉🎉.
For maximum optimization, we'll add AWS LifeCycles. Here we'll configure a set or rules governing the objects. Example; - After 2 months, transition from Standard to -IA
- After 6 months transition to S3 Glacier
- After 1 year transition to Deep Archive
- After 5 years, terminate.
Serverless Services
Finally, CynHealth wanted a web application to be have high performance, but be cost effective. Naturally, we'd deploy the application using EC2 instances, and for backend database we'd launch RDS MySQL Database Instances. But for cost effectiveness, let's try the serverless route.
First of all, our serverless platform has several departments;
- Compute:- AWS Lambda, AWS Fargate.
- Storage:- Amazon S3
- Database:- DynamoDB, AWS Aurora.
- API Proxy:- Amazon API Gateway.
- Integration:- Amazon SNS, Amazon SQS.
With that in mind, let's design the web application the serverless way.
Our web app may have some static content. Now accessing the content directly from S3 when the site is accessed would work, but that would be expensive. Amazon CloudFront is a much cheaper, faster and more secure option, where the requests would pass through it to S3, and cloudfront has its own local cache so retrieving data won't be that frequent.
For the compute section, instead of deploying EC2 instance, we'll use Lambda functions . The API Gateway will be used to access the Lambda functions securely.
For the database section, Amazon Aurora is a much cheaper option than the RDS MySQL database which was previously considered.
Well that was a long ride! I hope it wasn't a confusing one. In summary, always remember the AWS Cost Optimization Pillars;
- Right Size your instances
- Increase elasticity (ability to scale up and down)
- Use the right pricing model
- Optimize storage
- Measure, Monitor, Improve.
AWS tools are just our helpers when it comes to optimization. Understanding AWS products, pricing models and charging points is very crucial. See you soon!!

